A good way to optimize the function of your leadscrew product is to have your engineers collaborate with our engineering team during the design phase of your linear motion application.
We are able to recommend or develop specific thread forms for your unique application. When needed for the application, we are capable of making custom tooling to produce a special thread form with a specific lead (or pitch).
Noll is also capable of assisting you with your leadscrew assembly design. Our engineering staff is committed to working with you to provide your engineers with our specialized experience and insight to optimize the design phase of your product.
 At Noll, Design For Manufacturing (DFM) services are part of how we do business. Initial planning and consideration for the best manufacturing process reduces product cost and, in most cases, delivery time.
At Noll, Design For Manufacturing (DFM) services are part of how we do business. Initial planning and consideration for the best manufacturing process reduces product cost and, in most cases, delivery time.
Get us involved early so Noll can give you a real competitive edge. Together, we’ll increase the manufacturability of your product to save you money and speed up delivery.
Additionally, you can count on a quick turnaround when we provide first article (prototype) inspection for your approval.
If you have questions about our engineering capabilities, processes, or pricing, please call us at 805-543-3602 or click here to email.

LEADSCREW (pronounced: leed-screw) also, lead screw, lead-screw or screw drive. A Leadscrew is an assembly of a threaded shaft with a mating threaded nut.
The basic function of a leadscrew assembly is to convert rotary motion into linear motion. The threaded shaft is rotated with a motor or crank and the nut travels along the shaft. The resulting motion of the nut can drive a load.
Leadscrews are used in many industrial automation applications. There are many types of threads and mounting configurations used with leadscrews. Leadscrews or screw drives are a time proven, accurate and highly configurable mechanism for providing controlled linear motion.
Comparing leadscrews versus ballscrews:
An Acme leadscrew uses a threaded screw design with sliding surfaces between the nut and screw.
A Ball leadscrew uses a ball nut which houses one or more circuits of recirculating steel balls which roll between the nut and screw.
Comparing Rolled threads versus Machined threads:

The grain structure of a rolled thread is parallel to the surface of the thread. This process results in a strong thread in the axial direction.
A Rolled thread is manufactured using a different process than the Machined or Ground thread. Rolling is a cold forming process, similar to forging, which moves the material to conform to a die. There is zero material removal using the rolling process. The grains of the material flow as the threads are formed. Rolled threads posess an ideal grain structure for axial shear strength which increases the load bearing capacity.

The grain structure of a machined or ground thread is parallel to the axis of the thread. Machined and Ground threads are manufactured using a material removal process. This process results in a weaker thread in the axial direction.
Some of the reasons why the thread rolling process is beneficial:
In order to determine the correct leadscrew, you will need to know a little about your application.
To choose the leadscrew type and size, to fit your application, provide us with:
If you do not know some or all the information required, contact Noll Incorporated and let our experienced engineers help you with your design. The best way to request a quote or order a leadscrew is to FAX or eMail a print or drawing of your design.
Selecting the Right Thread Size:
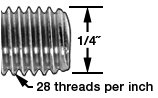
Inch threads are specified with a size (Diameter) and the number of threads (Threads Per Inch, or TPI for short). For example, 1/4-28 indicates a 1/4″ diameter screw with 28 threads per inch.
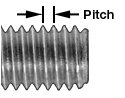
Metric threads are specified with a size and thread pitch instead of a thread count. The thread pitch is the distance between threads. For example, M8 x 1.25 indicates an 8mm diameter screw with a 1.25mm thread pitch.